Infraspinatus Taping
Taping your infraspinatus can help provide your damaged tissues with bonus support and protection. This works to help prevent re-injury. Sports tape can be worn during all of your daily activities but is particularly effective when worn during exercise.
The taping application below is just an example. While we found it effective for infraspinatus injuries, please feel free to try out various applications in order to find the one that works best for you. There are plenty of tutorials and instructions online. Just remember to pay attention to your pain. If you're feeling pain in a specific area of your shoulder, apply the tape there.
The taping application below was applied over clothing for demonstration purposes. It is intended to be applied directly over the skin. Since the tape needs to be applied to the back of your shoulder, you will likely need someone to help you. Before taping your shoulder, make sure the area is dry and free of any lotions, oils or dirt.
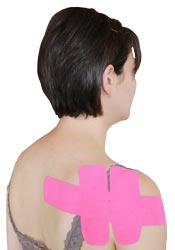
1. Take a full length piece of tape (about 10 inches) and tear the backing off one end.
2. Using no stretch, anchor the tape just below the bone that protrudes from the side of your shoulder.
3. Remove the rest of the backing from the tape, and using 25% stretch, pull the tape towards the back of your shoulder, going just below where the top of the shoulder blade protrudes. Lay down the end of the tape with no stretch.
4. Take another 10 inch piece of tape and cut it in half, rounding the corners, so you have two 5 inch strips of tape.
5. Take one of the 5 inch strips and tear the backing in the middle, peeling it away so you are holding onto the two anchor ends.
6. Using 80% stretch in the middle and no stretch at the ends, apply the tape vertically along the side of your shoulder.
7. Take the other 5 inch strip of tape and tear the backing in the middle, peeling it away so you are holding onto the two anchor ends.
8. Using 80% stretch in the middle and no stretch at the ends, apply the tape vertically right beside the one you just applied, but closer to your shoulder blade.
9. Rub the tape into your skin to make sure it sticks.
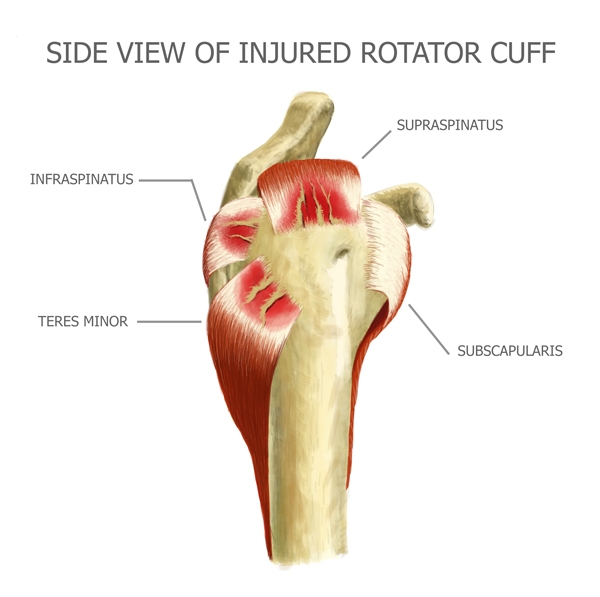
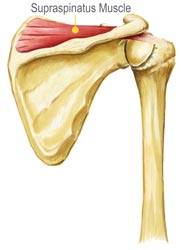
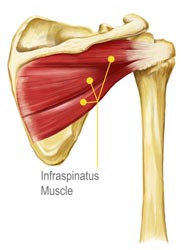
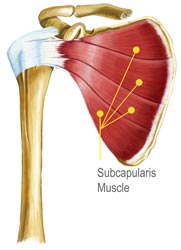
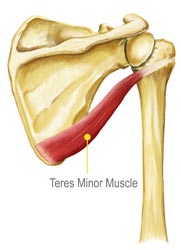
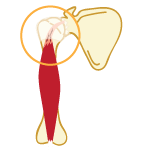
Infraspinatus Tear Diagnosis

First, your doctor will ask you to describe your symptoms and how long you've been experiencing them. You may also discuss your medical history, in case your current injury is related to a past injury or another medical condition. Then your doctor will examine your shoulder. You may have to change into a gown so your doctor can compare your injured shoulder to your healthy shoulder. This will indicate if there is inflammation or any deformity present. In order to confirm a diagnosis, your doctor may send you to get an MRI or ultrasound. These imaging tests can indicate whether there is a tear, how severe the tear is, and how long you've had the tear. Your doctor may also send you to get x-rays if he or she suspects you may have another condition, such as arthritis. While soft tissue (like the infraspinatus) shows up in MRI and ultrasound imaging tests, it does not show up on x-rays.
Surgery
Most infraspinatus tears won't require surgery in order to heal. Surgery should always be considered a last resort. However, if you have a full tissue tear (called a rupture) or if conservative treatment (RICE, pain medication, physiotherapy) has failed to help you after 6-12 months, you may be a good candidate for surgery. This also applies to people who have complex tears involving more than one muscle or tendon.
Infraspinatus repair surgery is usually successful for those who are relatively young and healthy. You will most likely undergo something called arthroscopic surgery, which involves a tiny tube with a camera at the end being inserted into a small incision in your shoulder. This will allow the surgeon to look at the tissue damage and perform the surgery. Several other small incisions will be made in the shoulder for the surgical tools. During the procedure, the torn tissue will be sewn back together. If the injury involves any tissue that was detached from the bone, this will be secured back in place.
If your tear is quite large or you have a complex rotator cuff tear, your surgeon may have to perform open repair surgery. In an open repair procedure, an incision is made in the shoulder and the deltoid muscle is moved to allow the surgeon to perform the repair. After the procedure, you will be stitched up and a dressing will be applied to your shoulder.
The latest procedure when it comes to rotator cuff surgery is called a mini-open repair. This procedure eliminates the need to detach and move the deltoid, as it involves a smaller incision as well as the latest tools. First, an incision is made and an arthroscope is used to look at the damage within the shoulder. If there are any bone spurs, they will be removed at this time. Then the arthroscope is removed and the tissue damage is repaired through the mini-open incision using surgical tools.
You will probably have to wear a sling for several weeks following the procedure. Recovering from infraspinatus surgery can take up to 6 months depending on the severity of the tear and the type of procedure you undergo. Physiotherapy can help you restore strength and range of motion to your shoulder following surgery.
Copyright 2011-2026 King Brand Healthcare Products® Limited. All Rights Reserved.
Ankle Ice Packs Comparision,
Back Ice Packs Comparision,
Elbow Ice Packs Comparision,
Foot Ice Packs Comparision,
Knee Ice Packs Comparision,
Leg Ice Packs Comparision,
Shoulder Ice Packs Comparision,
Wrist Ice Packs Comparision,
Ankle Injury Treatment,
Back Injury Treatment,
Elbow Injury Treatment,
Foot Injury Treatment,
Healing Therapy and Injury Treatment,
Knee Injury Treatment,
How to Tape Injuries.
King Brand
® ColdCure
® Cold Therapy ice packs and gels are the best solution to your ankle soft tissue injury. King Brand
® ColdCure
® RigiGel
® Ankle Wraps hold the cold longer, stay in place and are safer than any other product. Treat your ankle pain with King Brand
® for the best results.