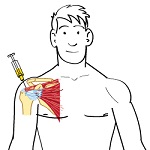
Infraspinatus Tendonitis
Because it has a poor mechanical advantage, the infraspinatus is a relatively weak muscle in most people. If it is called upon to suddenly perform heavy exertion, it can easily strain or tear. Some people have a minor strain of the infraspinatus tendon that continues almost unnoticed for years. They may experience slight discomfort when reaching for something on a high shelf or into the back seat of the car. However, when this minor lesion does not heal properly, it can set the stage for a more severe injury later.
When a strain of the infraspinatus tendon occurs, the person frequently feels nothing at the moment because the tendon is warmed-up or because the person is focused in the heat of the moment during an athletic activity. Later that day or the next morning, difficulty putting on a shirt or coat may occur, as the arm is lifted up and out to the side.
With infraspinatus tendonitis, pain is felt in the upper-arm region, sometimes slightly toward the back of the arm, but not always. When the injury is severe, pain can travel to the wrist. During the verification tests for this injury, pain will often be felt down the back, front, or outside of the upper arm and occasionaly over the scapula. Severe infraspinatus tendonitis sufferers may complain of pain down the arm as far as the wrist, but this pain pattern occurs only in extreme cases of this injury.
Two to three months of rest will sometimes allow infraspinatus tendonitis to heal, but more often it will remain for years, especially in an active person. Tendon injury exercise, along with rest may improve the condition. Treatment is usually recommended if rest and exercise don't elimate the pain in the course of a month. Hitting backhand in raquet sports is not a good idea while in treatment, nor are any exercises that cause pain such as push-ups and chin-ups.
What Is Infraspinatus Tendonitis
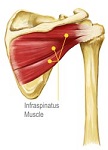
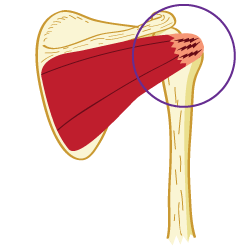
Tendons attach muscle to bone and is the focus for the "pull" of the muscle. When you damage it the muscle pulls part of the tendon away from the bone and the attachment point becomes frayed and sore. While the tendons themselves are enormously strong, the attachment point becomes frayed and sore. While the tendons themselves are enormously strong, the attachment to the bone is usually weaker and first to give. Tendonitis is very common at the shoulder. Only selected arm and shoulder movments hurt, the worst being putting your hand in your back pocket.
Physical Therapy
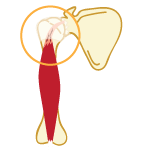
In tendonitis, some of the many fibres that make up the tendon snap and the broken ends curl back leaving a gap. Tendon grows slowly, so it's place is taken by scar tissue which does not have as good "pulling power" as the tendon does. The damaged fibres then re-attach themselves by forming scar tissue. Unlike fractures, where the repair is better than the original, the quality of repair for tendons can be poor. This is caused because of the formation of scar tissue, which sticks to the surrounding tissues and causes adhesions. These damage the surrounding muscule and restrict circulation, which is a vital part of the healing process. The result is that the tendon is more likely to injure again as a result of the poor quality of the mend. The physical therapist will work to correctly align the damaged and repairing fibres, gently stretch the shortened tendons and muscles, prevent the formation of adhesions, increase circulation and improve the quality of repair. Because the blood supply to tendons is poor, the speed of recovery is also slow. Treatment not only speeds repair and recovery, but can dramatically improve the quality of repair.
Forum Content from the Health Care Company King Brand®
Which should I use to treat Frozen Shoulder - Top or Side Shoulder Wraps?A customer asked, "Which should I use to treat Frozen Shoulder - Top or Side Shoulder Wraps?"
Re: Which should I use to treat Frozen Shoulder - Top or Side Shoulder Wraps?We typically recommend the Top Shoulder products to treat Frozen shoulder.
You can see the expected coverage zone shown in yellow by clicking the link below and scrolling down the page.
http://shop.kingbrand.com/product_info.php?products_id=340&REF=2160PV0.1522
The Top Shoulder BFST and Top Shoulder ColdCure have a large treatment area, and can treat most of the shoulder, focusing on the top area of the shoulder. This is usually ideal for treating frozen shoulder.
The BFST works to increase your blood flow and heal the soft tissue in the entire area that you treat. The ColdCure is extremely effective at reducing pain, swelling, and inflammation through the use of cold therapy.
More Info:
http://kingbrand.com/Frozen_Shoulder_Treatment.php?REF=2160PV440.1522
→ Click here for the the full King Brand® Forum
Copyright 2011-2026 King Brand Healthcare Products® Limited. All Rights Reserved.
Ankle Ice Packs Comparision,
Back Ice Packs Comparision,
Elbow Ice Packs Comparision,
Foot Ice Packs Comparision,
Knee Ice Packs Comparision,
Leg Ice Packs Comparision,
Shoulder Ice Packs Comparision,
Wrist Ice Packs Comparision,
Ankle Injury Treatment,
Back Injury Treatment,
Elbow Injury Treatment,
Foot Injury Treatment,
Healing Therapy and Injury Treatment,
Knee Injury Treatment,
How to Tape Injuries.
King Brand
® ColdCure
® Cold Therapy ice packs and gels are the best solution to your ankle soft tissue injury. King Brand
® ColdCure
® RigiGel
® Ankle Wraps hold the cold longer, stay in place and are safer than any other product. Treat your ankle pain with King Brand
® for the best results.